Raspberry PI RF 433 MHz Control Code
433MHz Radio Frequency Transceivers can transmit or receive radio signals. You can wirelessly control electronic components with radio signals, or get data from sensors. Control your electronic components by sending commands in binary numbers (ones and zeros). Find out the exact commands by reading the datasheet of the controllable device. If the commands you find in your device's datasheet are not binary, you can use online converters or a Windows Calculator to convert commands into binary.
Before running the python codes you need to install the required library's.
Please download this setup file and run
the script as superuser (sudo ./setup.sh).
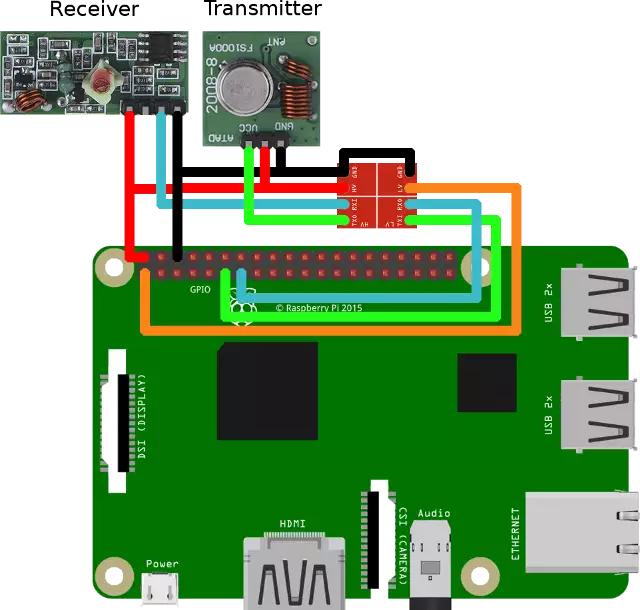
Required hardware
- Raspberry PI
- 433MHz Receiver
- 433MHz Transmitter
- Logic Level Converter
Source code to install on controller
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import argparse
import logging
from rpi_rf import RFDevice
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO, datefmt='%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S',
format='%(asctime)-15s - [%(levelname)s] %(module)s: %(message)s',)
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='Sends a decimal code via a 433/315MHz GPIO device')
parser.add_argument('code', metavar='CODE', type=int,
help="Decimal code to send")
parser.add_argument('-g', dest='gpio', type=int, default=17,
help="GPIO pin (Default: 17)")
parser.add_argument('-p', dest='pulselength', type=int, default=None,
help="Pulselength (Default: 350)")
parser.add_argument('-t', dest='protocol', type=int, default=None,
help="Protocol (Default: 1)")
args = parser.parse_args()
rfdevice = RFDevice(args.gpio)
rfdevice.enable_tx()
if args.protocol:
protocol = args.protocol
else:
protocol = "default"
if args.pulselength:
pulselength = args.pulselength
else:
pulselength = "default"
logging.info(str(args.code) +
" [protocol: " + str(protocol) +
", pulselength: " + str(pulselength) + "]")
rfdevice.tx_code(args.code, args.protocol, args.pulselength)
rfdevice.cleanup()
Source code to install on controller
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import argparse
import logging
from rpi_rf import RFDevice
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO, datefmt='%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S',
format='%(asctime)-15s - [%(levelname)s] %(module)s: %(message)s',)
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='Sends a decimal code via a 433/315MHz GPIO device')
parser.add_argument('code', metavar='CODE', type=int,
help="Decimal code to send")
parser.add_argument('-g', dest='gpio', type=int, default=17,
help="GPIO pin (Default: 17)")
parser.add_argument('-p', dest='pulselength', type=int, default=None,
help="Pulselength (Default: 350)")
parser.add_argument('-t', dest='protocol', type=int, default=None,
help="Protocol (Default: 1)")
args = parser.parse_args()
rfdevice = RFDevice(args.gpio)
rfdevice.enable_tx()
if args.protocol:
protocol = args.protocol
else:
protocol = "default"
if args.pulselength:
pulselength = args.pulselength
else:
pulselength = "default"
logging.info(str(args.code) +
" [protocol: " + str(protocol) +
", pulselength: " + str(pulselength) + "]")
rfdevice.tx_code(args.code, args.protocol, args.pulselength)
rfdevice.cleanup()
